DPGs for DPI
Digital public infrastructure (DPI) — which refers to a secure and interoperable network of components that include digital payments, ID, data exchange, and other foundational systems—is essential for participation in markets and society in a digital era. DPI is needed for all countries to build resilient and innovative economies and for people's well-being. DPI can be built by adopting and adapting digital public goods (DPGs). This collection features DPGs that are being implemented by countries as part of their DPI and reviewed by the DPGA Secretariat's technical team as part of the solutions being recognized as a digital public good.
It is limited to solutions that are relevant to the four DPI use cases listed above. This collection will continue to grow as more solutions become DPGs.
Digital Public Goods
Use Cases
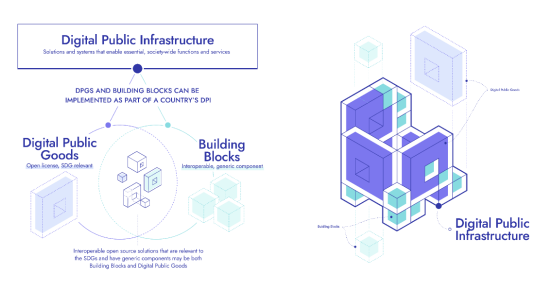
GovStack Definitions: Understanding the Relationship between Digital Public Infrastructure, Building Blocks & Digital Public Goods

Six ways countries are implementing safe, inclusive, and interoperable DPI with open source

UN High Impact Initiative: Digital Public Infrastructure
What is Digital Public Infrastructure?

The Mojaloop moment: Expanding financial inclusion

Open Source Principles in DPI. Ensuring Interoperability, Security, and Trust.

X-Road® as a Digital Public Good – enabling digital transformation in emerging countries
